關於VTP,有些被我想複雜了,有些卻被我想簡單了。
參考文件:Understanding VLAN Trunk Protocol (VTP)
1.
這個被我想複雜了
VTP = Layer2 protocol, why IP here ?
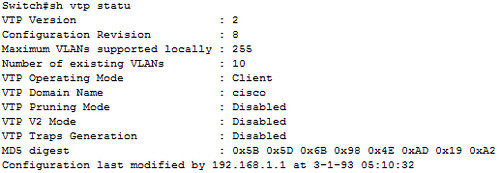
以為這之中有甚麼驚人的秘密,的確!根本就沒有秘密...
這個IP是"Updater Identity",識別而已,並不參與VTP的運作。

Code = 0x02 = advertisement
2.
這被我想簡單了
我以為VTP server就一直把advertisement packets丟出去,client就一直撿起來compare這樣。
但事實上client是會發出advertisement request的。
advertisement request packet format :

Code = 0x03 = advertisement request
而且還會針對沒被update的部分發出request,有聰明。
3.
這點我到現在還不明白:為什麼明明是layer2的 "frame",cisco要把它叫做 "packet"?
知道的大德請不吝賜教~~~~
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
同場加映